The Seventh-day Adventist Church has a representative form of structure that connects its 90,000-plus congregations across the globe and gives its members a part in decision-making. Though the Church was incorporated in 1863, this system came about during the church’s reorganization from 1901 to 1903. It includes four levels of organization.
This system is unique compared to the organizational structure of other denominations.
It does not function with one person at its head (an episcopal form of organization), or even a group of leaders making decisions for the whole body (a Presbyterian form of organization). Instead, authority comes from the church members, who elect delegates to serve on the world church level.
The purpose for this kind of structure?
A denomination united with a worldwide mission needs an efficient way to carry it out. This structure ensures that every church has the resources to serve its members and lead people to Jesus.
So let’s get a little more detail by looking at:
- The four levels of organization in the Adventist Church
- The way decisions are made for the world church
- The financial structure of the Adventist Church
What are the four levels of organization in the Adventist Church Structure?
Levels of organization in the Adventist Church are like concentric circles. Starting from the smallest circle in the middle, they are:
These levels link up a worldwide network of churches. Each one exists to serve the levels right below it, better enabling the local leadership to serve their individual members. In turn, the members can focus on their mission—sharing Jesus.
Local church organization
The local church is a group of believers who love Jesus and live out the teachings of His Word. They receive spiritual guidance from a pastor and come together on a regular basis for worship services. They also get to participate in the church’s decision-making process through business meetings, as needed.
All church members can attend and vote in church business meetings. The kinds of decisions made during those meetings include:
- Church membership
- Financial decisions
- Discipline
- Election of leaders
- Evangelism efforts
 Sometimes, one function of these meetings happens on Sabbaths during the worship service. For example, after a baptism, the pastor will call for a vote to accept the baptized individual into membership—it’s simply a formal way of celebrating the new member’s acceptance into the church, showing unanimous support.
Sometimes, one function of these meetings happens on Sabbaths during the worship service. For example, after a baptism, the pastor will call for a vote to accept the baptized individual into membership—it’s simply a formal way of celebrating the new member’s acceptance into the church, showing unanimous support.
But financial and business matters, or issues that require significant discussion, are handled at other times.
In church business meetings, members have the opportunity to vote for their leaders. These leaders form the church board, which handles the administrative matters of the congregation. It’s like a board of directors for a company.
In Adventist Churches, the congregation doesn’t directly hire their pastor. Rather, the local conference provides the church with candidates to choose from and takes care of the hiring process.
Though the pastor provides spiritual support and leadership, his authority—and that of the church board—does not exceed that of the business meeting. In the end, the church members’ votes have the greatest authority.
Local conference
The local conference consists of a group of churches within a certain region, such as a state or metropolitan area. Its leaders are elected by a delegation of church members during a constituency session.
What’s a constituency session? We can compare it to the business meeting of the local church. Major decisions for the conference are made at this session.
Local churches send representatives, who have been voted by the members (or constituents), to attend the constituency session. In this way, each church takes part in the conference’s decisions.
The local conference fulfills these roles:
- Hiring of pastors
- Distribution of tithe money to pay pastors
- Authorization of local churches
- Ownership of church property
- Administration of Adventist boarding schools
- Conference-wide plans for community outreach
Union conference
A union conference is a group of local conferences within a region. It usually covers a few states, provinces, or territories.
For example, the North Pacific Union Conference in the United States covers six local conferences: Alaska, Idaho, Montana, Oregon, Washington, and Upper Columbia (the northeastern region of Washington state).
Like the local conference, the union conference holds constituency meetings. But this time, the local conference chooses the delegates from among the church members.
What is the role of the union conference?
It handles administrative matters for its region. It also ordains (authorizes) pastors and operates union institutions, such as universities.
And don’t forget evangelism! Each level of the church structure is designed to provide support in fulfilling the mission to spread the good news about Jesus.
General Conference and its divisions
The General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland, has administration over all Adventist churches across the globe—known as the world church. It has 13 divisions with regional offices. The leaders of these divisions assist the work of the General Conference in planning and providing resources for their respective geographical areas and regions.
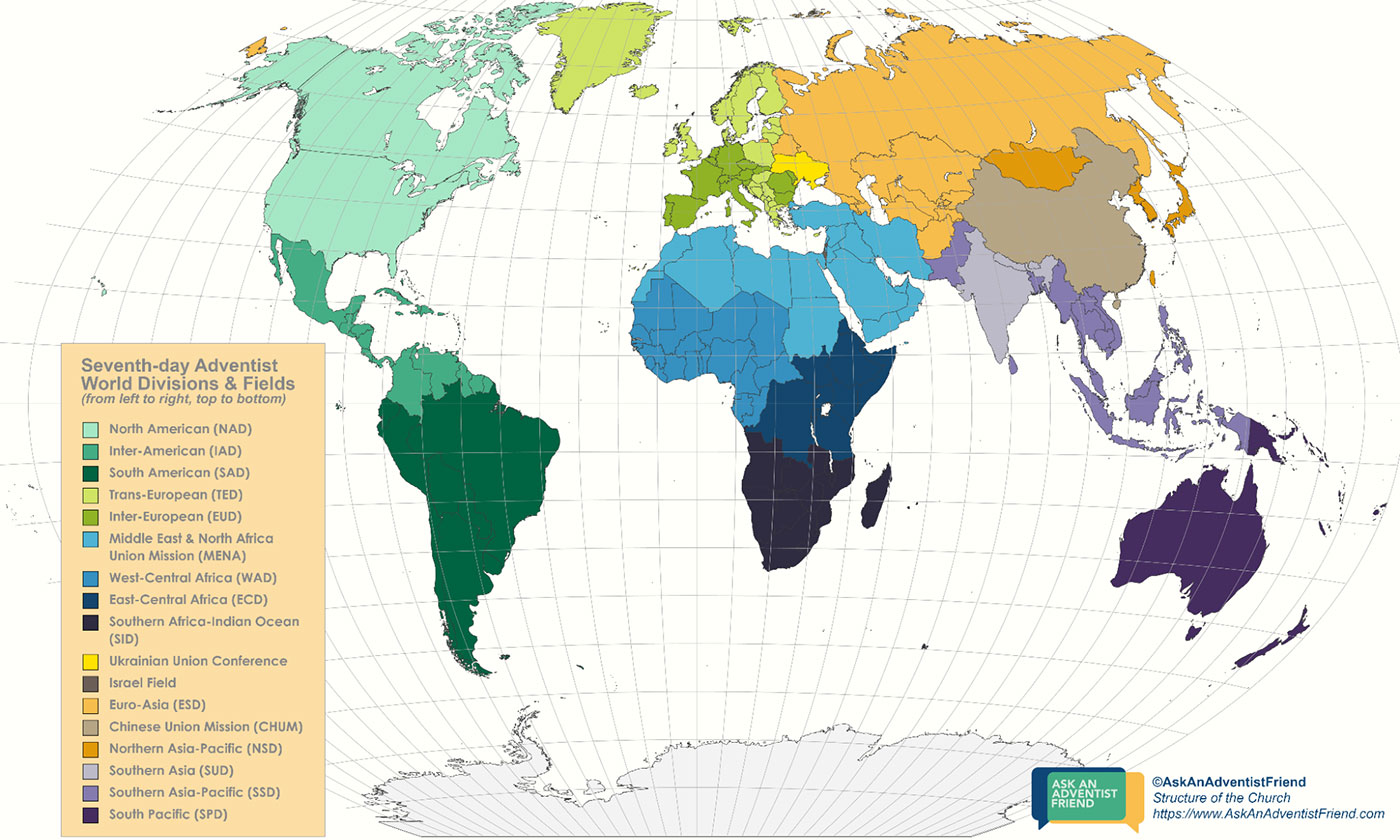
The divisions are:
- East-Central Africa Division(ECD)
- Euro-Asia Division(ESD)
- Inter-American Division (IAD)
- Inter-European Division (EUD)
- North American Division (NAD)
- Northern Asia-Pacific Division (NSD)
- South American Division (SAD)
- South Pacific Division (SPD)
- Southern Africa-Indian Ocean Division (SID)
- Southern Asia Division (SUD)
- Southern Asia-Pacific Division (SSD)
- Trans-European Division (TED)
- West-Central Africa Division (WAD)
You’re probably wondering what the General Conference does.
The General Conference deals with membership of union conferences, global policies, and questions related to fundamental beliefs. Delegates vote on these issues during a General Conference session every five years.
The highest decision-making authority in the Adventist Church rests in these sessions.
So, how exactly are these decisions made?
How are decisions made for the world church?

Photo by Element5 Digital on Unsplash
Delegates from around the world help make major decisions for the world church in accordance with the Bible. They come together every five years during a General Conference session that takes place in North America. This means that every church member is represented in the decisions.
Around 2,500 delegates attend the sessions and participate in voting traveling from their different parts of the world.
Of these delegates, at least half are regular church members, pastors, and teachers. Each union conference gets to select a certain number of church members as delegates.
In other words, almost any Adventist can be a delegate!
The other half are church leaders who represent institutions and committees worldwide.
During the session, the delegates discuss an agenda prepared by the General Conference executive committee and vote on the matters. They also elect General Conference leaders the conference president and world church officers.
But here’s the most important aspect:
Each stage of the decision-making process involves much prayer and Bible study.
Church leaders and delegates seek the Holy Spirit’s guidance because they realize that Jesus is their ultimate leader. They desire every decision to uphold the Bible and further the church’s mission.
What is the financial structure of the Adventist Church?
The Adventist Church operates as an official non-profit organization. All its employees and programs are supported by tithes and offerings/donations. It bases its financial structure on the New Testament church, which gathered money into a central location and distributed it to local congregations:
“And all who believed were together and had all things in common. And they were…distributing the proceeds to all, as any had need” (Acts 2:44–45, ESV).
In short, monetary support for the New Testament church came from the members.
According to the biblical model, Adventist church members return tithe—a term in the Bible that means “one-tenth.” Because God owns everything, we are stewards of His money and gladly return to Him the ten percent of our income that He asks for (Deuteronomy 14:22; Malachi 3:10–12).

Photo by Steve Johnson on Unsplash
But tithe is not used for just anything. It has a special purpose.
The tithe supports those who serve as pastors and missionaries, just like it supported the priests in the Old Testament and the church leaders in the New Testament (Numbers 18:21; 1 Corinthians 9:13–14).
Church leadership gathers the tithe and sends it to their local conferences. From there, it is distributed to pay pastors. This plan prevents the challenge of churches with many members being able to provide larger salaries than those with fewer members.
To learn more about Adventist beliefs related to tithe, check out this page on stewardship.
Then, there’s offerings.
An offering is a voluntary gift of money given to God (Exodus 35:29; 2 Corinthians 8:2–4). Sometimes, the giver assigns the offering to go toward a certain project or need.
But unassigned offerings are distributed according to the Combined Offering Plan. Here’s how it works:
About 50% of the offerings remain at the local church, 20 to 30% support regional mission, and 20% go to the General Conference, which distributes it to worldwide mission projects.
In this way, the world church helps each individual congregation—regardless of size or location—to accomplish its mission.
The Adventist Church’s structure is all about its mission
The Adventist denomination’s structure is unique in the way that it provides for the needs of its worldwide network and gives every member a part in vital decisions. No doubt, the Holy Spirit guided us to this plan.
This structure helps the church to function and fulfill its purpose: enabling church members to live out their mission as God’s people.
But even with all the levels of organization, we must remember one central point:
Jesus is the guide and leader of the church.
The structure is there to help us carry out His plans in the best way possible.
Find a Church
If you’re interested in finding a local Adventist church near you, you can use the Adventist Locator provided by the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists.
Related Articles
More Answers
Everything You Need to Know About an Adventist Church Potluck
Every so often, usually on a schedule ranging from once a week to once a month to once a quarter, an Adventist church will have “fellowship dinners,” often casually referred to as potlucks.
The Seventh-day Adventist Hymnal
The Seventh-day Adventist Hymnal is a songbook used worldwide by many Adventist congregations during their worship services. Since its publication in 1985, it has helped foster praise to God while reminding church members of our mission and drawing them closer to Jesus.
What Are Seventh-Day Adventist Sermons Like?
In nearly every Seventh-day Adventist Church, the sermon is the focal point of the main service—similar to many Protestant Christian denominations. It is a time of biblical instruction by the pastor, who shares what they’ve been studying in the Bible and preparing over the previous week.
Who Are Adventists
The Seventh-day Adventist Church—“Adventists” for short—is a Christian denomination of ordinary people who seek to follow Jesus and live out His mission in this world. Established in 1863, we hold to the Protestant principle of sola scriptura, which means the Bible guides everything we do.
Why is the Great Controversy in my mailbox?
Every year, households across North America receive free copies of a 150-year-old book, The Great Controversy. Millions more are shared around the world.
How do Adventists choose what to eat?
Food blogs overwhelm the internet; food fads are all the rage; and copycat and healthy versions of food are the subject of many a get-together.
Didn’t find your answer? Ask us!
We understand your concern of having questions but not knowing who to ask—we’ve felt it ourselves. When you’re ready to learn more about Adventists, send us a question! We know a thing or two about Adventists.










